
#10.#"The sum of the oxidation numbers in a polyatomic ion"#"is equal to the charge of the ion. #9.#"The sum of the oxidation numbers of all of the atoms"#"in a neutral compound is 0."# #8.#"The oxidation number of a Group 17 element in a binary compound is -1."# #7.#"The oxidation number of a Group 2 element in"#"a compound is +2."# #6.#"The oxidation number of a Group 1 element"#"in a compound is +1."# #5.#"The oxidation number of O in its"# compounds #"is usually -2, but it is -1 in peroxides."# #4.#"The oxidation number of H is +1, but it is -1 in when"#"combined with less electronegative elements."# #3.#"For a given bond, X-Y, the bond is split to give "X^+#"and"#Y^-#, #"where Y is more electronegative than X."# #2.#"The oxidation number of a mono-atomic ion is equal"#"to the charge of the ion."#
#Hydroxide oxygen charge free
#1.#"The oxidation number of a free element is always 0."# I do not propose that you learn them verbatim. Here are some rules taken from a prior answer.they are included as reference.
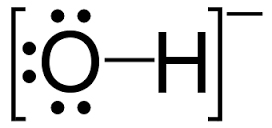
#H-O^(-)#.this is split to give #H^+# and #O^(2-)#.and thus we get oxidation numbers of #O(-II)# and #H(+I)#.of course the sum of the oxidation equals the charge on the ion. For example, the oxygen in water has no charge, however, in the hydroxide ion, which is the most common species acting as a base, bears a negative charge. The sum of the oxidation numbers is equal to the charge on the ion or the molecule, and of course this charge might be ZERO. The bond, the two electrons binding an element or ion are broken, with the charge, the electron assigned to the most electronegative atom. The oxidation number is a fictitious charge of atoms involved in chemical bonds that reflects electronegativity.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
